The production process of hot-rolled solid ingots is to roll them into hollow tubes with no seams around them. Hot rolling can be used to produce seamless steel pipes made of carbon steel, alloy, high alloy steel, and some non-ferrous metals, with an outer diameter range of 16 to 1600 mm and a wall thickness of 2 to 200 mm.
In addition to round-section pipes, there are also various special-section pipes and variable-section pipes. In addition to being finished pipes, hot-rolled seamless steel pipes can also be used as pipe materials for cold drawing and cold-rolled pipes (see cold rolling and cold drawing of pipes). Seamless steel pipes produced by hot rolling account for 80% to 90% of the production of seamless steel pipes.
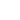
The process flow of modern hot-rolled steel pipes is:
The billets used for hot-rolled steel pipes include ingots, continuous casting billets, rolled billets, forged billets, and hollow casting billets. The basic process of hot-rolled steel pipes is:
(1) Punch the ingot or billet into a hollow thick-walled rough pipe on a punching machine. The methods of perforating the tube blank are divided into two-roller oblique rolling perforation, pressure perforation, push rolling perforation, three-roller oblique rolling perforation, etc.
(2) The rough tube is thinned on the stretching machine and stretched into a rough tube with a wall thickness close to that of the finished tube. The rough tube stretching, is, rough tube rolling methods include automatic tube rolling, continuous tube rolling, three-roll and two-roll tube rolling (see tube material rolling and stretching), periodic tube rolling, and jacking.
(3) The rough tube is finished on the finishing mill to become a finished tube. The rough tube finishing rolling includes tube leveling and tube sizing to improve quality, tube diameter reduction, and tube hot expansion to expand product specifications.
The units for producing hot-rolled seamless steel tubes can be different according to the different production methods and equipment used in the three basic processes of perforation, stretching, and finishing. Different units are named after the rolling mill that stretches the rough tube into the rough tube. For example, an automatic pipe rolling mill is called an automatic pipe rolling mill unit, a continuous pipe rolling mill is called a continuous pipe rolling mill unit, a machine that rolls rough pipes on a three-roll (or two-roll) inclined rolling and stretching mill is called a three-roll (or two-roll) pipe rolling mill unit, a machine that rolls pipes on a periodic pipe rolling mill is called a periodic pipe rolling mill unit, and a machine that rolls pipes on a CPE pipe jacking machine is called a CPE pipe jacking unit.
Post time: Oct-16-2024